Researchers at the Joint Quantum Institute (JQI) have created the first silicon chip that can reliably constrain light to its four corners. The effect, which arises from interfering optical pathways, isn't altered by small defects during fabrication and could eventually enable the creation of robust sources of quantum light.
That robustness is due to topological physics, which describes the properties of materials that are insensitive to small changes in geometry. The cornering of light, which was reported June 17 in Nature Photonics, is a realization of a new topological effect, first predicted in 2017.
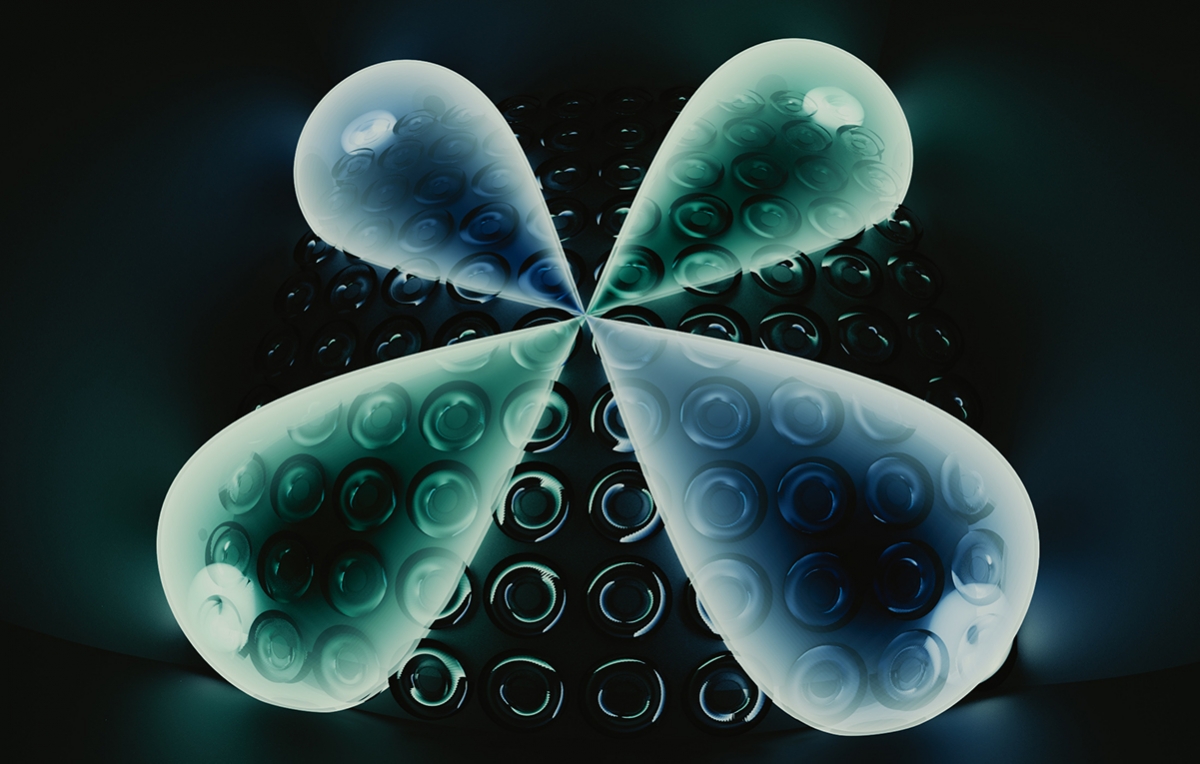 A new, grooved silicon chip keeps light in the corners using the physics of quadrupoles and topology. (Credit: E. Edwards/JQI)
A new, grooved silicon chip keeps light in the corners using the physics of quadrupoles and topology. (Credit: E. Edwards/JQI)
In particular, the new work is a demonstration of quadrupole topological physics. A quadrupole is an arrangement of four poles—sinks and sources of force fields such as electrical charges or the poles of a magnet. You can visualize an electric quadrupole by imagining charges on each corner of a square that alternate positive-negative-positive-negative as you go along the perimeter.
The fact that the cornering arises from quadrupole physics instead of the physics of dipoles—that is, arrangements of just two poles—means it a higher-order topological effect.
Although the cornering effect has been observed in acoustic and microwave systems before, the new work is the first time it’s been observed in an optical system, says Associate Professor and JQI Fellow Mohammad Hafezi, the paper’s senior author. "We have been developing integrated silicon photonic systems to realize ideas derived from topology in a physical system," Hafezi says. "The fact that we use components compatible with current technology means that, if these systems are robust, they could possibly be translated into immediate applications."
In the new work, laser light is injected into a grid of resonators—grooved loops in the silicon that confine the light to rings. By placing the resonators at carefully measured distances, it's possible to adjust the interaction between neighboring resonators and alter the path that light takes through the grid.
The cumulative effect is that the light in the middle of the chip interferes with itself, causing most of the light injected into the chip to spend its time at the four corners.
Light doesn’t have an electric charge, but the presence or absence of light in a given resonator provides a kind of polar behavior. In this way, the pattern of resonators on the chip corresponds to a collection of interacting quadrupoles—precisely the conditions required by the first prediction of higher-order topological states of matter.
To test their fabricated pattern, Hafezi and his colleagues injected light into each corner of the chip and then captured an image of the chip with a microscope. In the collected light, they saw four bright peaks, one at each corner of the chip.
To show that the cornered light was trapped by topology, and not merely a result of where they injected the lasers, they tested a chip with the bottom two rows of resonators shifted. This changed their interactions with the resonators above, and, at least theoretically, changed where the bright spots should appear. They again injected the light at the corners, and this time—just as theory predicted—the lower two bright spots showed up above the rows of shifted resonators and not at the physical corners.
Despite the protection from small changes in resonator placement offered by topology, a second, more destructive fabrication defect remains in these chips. Since each resonator isn't exactly the same, the four points of light at the corners all shine with slightly different frequencies. This means that, for the moment, the chip may be no better than a single resonator if used as a source of photons—the quantum particles of light that many hope to harness as carriers of quantum information in future devices and networks.
"If you have many sources that are forced by topology to spit out identical photons, then you could interfere them, and that would be a game-changer," says Sunil Mittal, the lead author of the paper and a postdoctoral researcher at JQI. "I hope this work actually excites theorists to think about maybe looking for models that are insensitive to this lingering disorder in resonator frequencies."
Story by Chris Cesare
Hafezi and Mittal also have affiliations in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, as well as the Institue for Research in Electronics and Applied Physics. Hafezi is also an associate professor in the Department of Physics.